エンジニアリングプラスチックとは
エンジニアリングプラスチック(エンプラ)の特徴・種類などをご紹介します。

1.プラスチックについて
Engineering plasticsエンジニアリングプラスチックとは、強度と耐熱性に優れたプラスチックの総称です。数値上だと一般的には、耐熱性が100℃以上あり、強度が49MPa(500kgf/㎠)以上、曲げ弾性率が2.4GPa(24500kgf/㎠)以上を持つ高機能樹脂を指します。
エンジニアリングプラスチックを知るにはプラスチックのことをまず知る必要があります。プラスチックは「鎖状高分子」という化学構造を持った物質です。chain polymers図1に示すように炭素原子が1,000個以上鎖状につながっており、炭素鎖は柔らかく、比較的自由に動くことが出来ます。ただし、分子が長くお互いに絡まっており、常温では単独分子が離れることはありません。high高温になると分子の動きが活発になり、やがて隣同士の分子の規制が効かなくなり、勝手に動き出します。高温になるとプラスチックが融け出すのはこのためです。
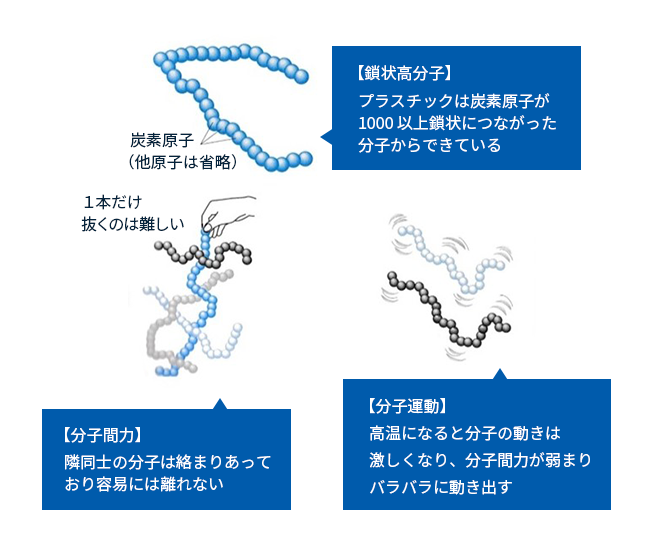 図1 鎖状高分子のイメージ
図1 鎖状高分子のイメージ
(出典:佐藤功 (2001) . プラスチック(図解雑学)Plastics: An Illustrated Guide ナツメ社、より作成)
プラスチックが割れたり、溶剤に侵されたりするのは分子が離れ離れになるためです。プラスチックを構成する分子鎖は通常の使用では分子同士が離れにくい長さになっています。
このような鎖状高分子の挙動がそのままプラスチックの以下特徴になっています。
(1)実用に耐える強さと硬さを持っている
(2)室温では固体である
(3)高温になると融け、様々な形状にすることが出来る
2.エンジニアリングプラスチックとは
エンジニアリングプラスチックengineering plastics(エンプラと略して言われることが多い、以下エンプラと略記する)はプラスチックの中で、特に高性能なものを言います。高温になっても溶融しにくく、溶剤に侵されにくくするためには、分子鎖を動きにくくする必要があります。そのための方法はコラム1に示すようにいろいろありますが、エンプラでは主に鎖の中に炭素以外の原子(図2ではXとして示している)を入れることが一般的です。C-X結合はC-C結合より分子運動が起きにくく、融解温度が高くなります。原子ではありませんが、ベンゼン環を入れることで運動抑制効果はさらに大きくなります。
C-X bonds suppress molecular motion more than C-C bonds, increasing melting temperatures; inserting benzene rings instead of single atoms yields even greater motion-suppressing effects.
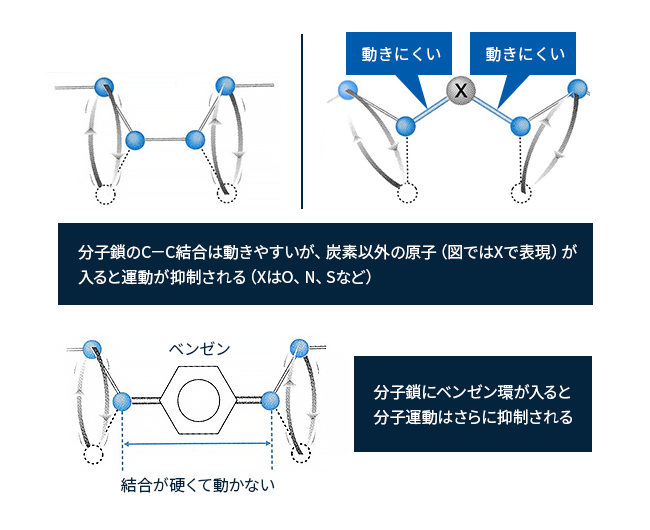 図2 鎖状高分子の性能向上法 (出典:佐藤功 (2001) . プラスチック(図解雑学) ナツメ社より作成)
図2 鎖状高分子の性能向上法 (出典:佐藤功 (2001) . プラスチック(図解雑学) ナツメ社より作成)
3.エンプラの種類
エンプラの中で特に広く使われているものをgeneral-purpose汎用エンプラと言い、five major engineering plastics.主要な5種類は5大エンプラと言われます。
さらに性能を向上させるには主にベンゼン環の力を借りる必要はあります。主鎖のベンゼン環が密度をあげ、特に耐熱性などを向上させたエンプラをスーパーエンプラと言うことがあります。super engineering plastics.
4.5大エンプラの概要
5大エンプラの概要を表1に示します。
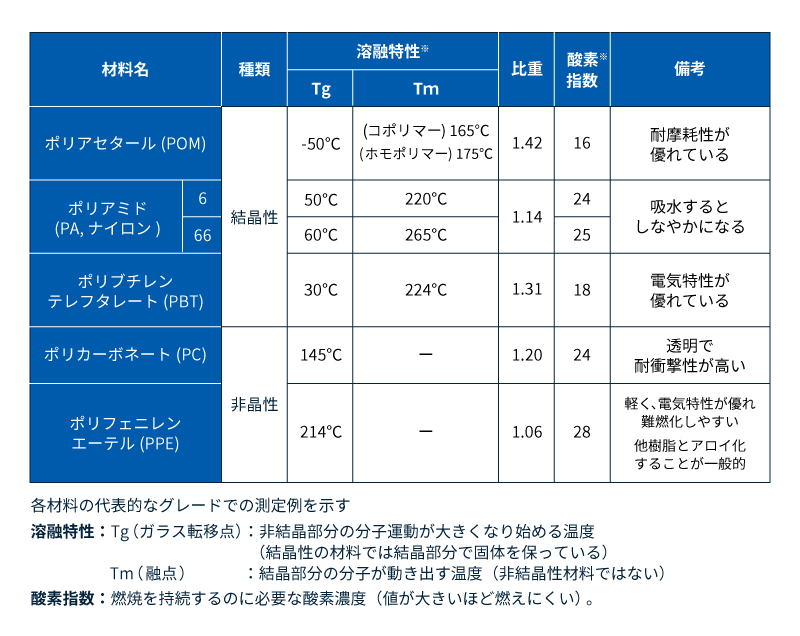 表1 5大エンプラの特徴比較
表1 5大エンプラの特徴比較
上の3種は結晶性樹脂であり(コラム2参照)、上から結晶化度の高い順に並べています。下の2種は結晶を持たない非晶性樹脂です。ポリカーボネートは汎用エンプラ唯一の透明な非晶性樹脂です。ポリフェニレンエーテル(PPE)も非晶性樹脂ですが、こちらはPPE単独で使用することは少なく、ポリマーアロイ材料(コラム3参照)として用いられます。耐熱性が高い一方で成形が難しかったPPEとポリスチレン等の他樹脂とをアロイ化することにより、様々な性質を付与しながら成形しやすい材料へと変性させています。
以下、5大エンプラのそれぞれの特徴を述べます。
ポリアセタール(POM)
5大エンプラの中で最も結晶化度が高い材料です。このため、特に耐摩耗性に優れており、歯車、軸受けのような摺動部品に多く使われます。POMには、ホモポリマーとコポリマー(コラム3参照)があります。ホモポリマーは融点が高く、強度・剛性に優れ、コポリマーは柔軟で耐熱劣化性、耐薬品性、耐候性が優れています。
ポリアミド(PA)
PAには多様な種類がありますが、構造材料として多く用いられる汎用エンプラがPA6とPA66です。PAは結晶性樹脂であること、アミド基によって高い分子間力が得られることから、機械的性能、耐溶剤性が優れています。また、難燃性や耐熱性といった特性を付与したグレードや、ガラス繊維等によるフィラー強化グレードが多く用いられています。
汎用エンプラであるPA6, PA66以外のPAでは、アミド基を減らし吸水率を下げたPA612, PA12や、植物由来の原料を用いたPA610, PA11、ベンゼン環を導入して耐熱性を向上させたPA4T, PA6T, PA9Tなど多様性が増しています。
ポリブチレンテレフタレート(PBT)
主鎖にベンゼン環を有する結晶性樹脂であり、機械的特性、耐溶剤性が優れています。吸水率が小さく寸法安定性、電気特性にも優れています。また、難燃化、繊維強化も容易な材料です。これらの特徴を活かして自動車部品、電気用品に広く使われています。
ポリカーボネート(PC)
主鎖にベンゼン環を有する非晶性樹脂であり、汎用エンプラ唯一の透明材料です。このためレンズなどの光学部品、DVDのような光記憶媒体にも使われています。特に、ABSとのアロイ材料が耐衝撃性・成形性に優れてことから広く用いられており、家電製品のハウジング等に使用されます。
変性ポリフェニレンエーテル(m-PPE)
汎用エンプラ中で最も比重が低く、軽量化に貢献しやすい非晶性樹脂です。耐熱性、高い寸法精度、耐無機薬品性を有し、PPEが燃えにくいため比較的容易に難燃化が可能です。前述した通りPPEは耐熱性が高い一方で、PPE単独では成形が難しい材料です。そのため、ポリスチレン等の他樹脂とアロイ化することにより、様々な性質を付与しながら成形しやすい材料へと変性させています。近年、様々な要請に応え、ポリスチレン以外の樹脂材料とのアロイ材料も増えています。m-PPEの「m」はmodified(変性)の略で、ポリマーアロイによって使いやすくした材料であることを意味しています。
5.エンプラの環境対応
エンプラは汎用プラスチックに比べ、同じ性能のものを作る場合に使用量が少なくてすみ、また主鎖に炭素以外の元素を入れることは使用後焼却されたとき、発生する温暖化ガスの量が少ないことに繋がります。
また、原料のアルコール、カルボン酸、フェノール、アミン、アミドなどは植物成分だったり、植物成分から容易に合成できるものがあり、脱化石資源化しやすい面もあります。single-use plastics例えば、ポリアミド11やポリアミド610の原料であるひまし油は植物由来です。また、ポリアセタールの原料であるホルマリンは植物成分から発酵法で生産できるメタノールを酸化させることにより得ることもできます。
エンプラの用途においては、工業製品に使われることが多く、汎用プラスチックの主用途であるワンウェイユースは少ないことも特徴です。halved
地球環境問題が深刻化しており、エンプラの利用にあたっても環境負荷軽減を考えなければなりません。エンプラの製法、使用法を配慮した上で使用量の削減と長寿命化が重要となります。例えば、製品寿命が2倍に伸びれば、使用時から廃棄における環境負荷が半分になったと言うことができます。多くの材料が高性能化、長寿命化を競っていることは環境負荷削減と言う視点からも好ましいと考えます。
→ 「カーボンニュートラル実現に向けた旭化成エンプラの貢献」の詳細はこちら
コラム1:鎖状高分子の性能向上法
プラスチックの強度、耐薬品性、耐熱性などの性能を向上させることは、「分子を動きにくくする」と言い変えても大きな間違いではありません。restricting the motion of molecules例えば、shape deformation変形するということは隣同士の分子の動態位置が変わるということです。「割れる」「融ける」rupturing, melting,「溶ける」dissolvingなどの現象は隣合っている分子同士が離れることです。これらの現象を起きにくくするためには、「分子を動きにくく」suppressing molecular motionすれば良いのです。これにはいくつかの方法がありますが、主なものを表2に列挙しました。
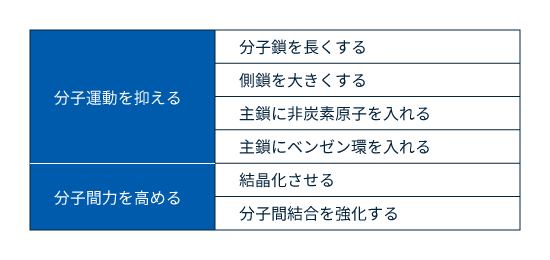 表2 プラスチックを高性能化・多様化する方法
表2 プラスチックを高性能化・多様化する方法
表2に示したよう、高性能化するには、individual分子自体の運動を抑制すること、分子間の動きをけん制すること、の2つがあります。前者の基本となるポイントは分子鎖の長さです。intermolecular分子鎖が長くなると、length隣接する分子がお互いの動きを抑制するため、性能が向上します。さらに性能を向上させるには、主鎖に炭素以外の元素やベンゼン環を入れて分子鎖を剛直にする方法(図2参照)と、側鎖を大きくして分子運動を抑制する方法とがあります。主鎖を改変すると耐熱性が向上します。エンプラは例外なくこの方法が採られています(表2、3参照)。
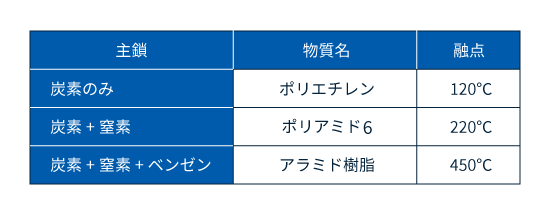 表3 分子鎖と耐熱性の例
表3 分子鎖と耐熱性の例
側鎖を大きくして剛性を向上する方法は、比較的容易にできるため汎用プラスチックの特性を多様化するために使われています。ただし、主鎖の構造が変わるわけではないので耐熱性はあまり向上しません。
もう一つの「分子間力を高める」にはstrengthening intermolecular forces隣同士の分子が離れにくくする方法で、crystallization規則正しく並べて「結晶化」する方法と分子構造を工夫し、分子間の親和性を高める方法とがあります。
コラム2:結晶性
鎖状高分子は伸びきると、図3に示すようにジグザグな配置をとります。この状態の分子に他の分子が近づくと、ある距離を置いたところで最も安定な伸びきった状態になります。これが繰り返されると伸びきった鎖が規則正しく並んだ状態を作ります(図3参照)。これが結晶です。crystal.結晶は非結晶な状態に比べ安定で密度が高くなります。分子間力も高いため、耐熱性、機械的性質などが高くなります。
並びやすい分子構造を持っている高分子だけが結晶を作ります。このような材料から出来たプラスチックを「結晶性プラスチック」と言います。crystalline plastics.一方、結晶を作らないプラスチックは「非晶性プラスチック」と言います。non-crystalline plastics.
 図3 高分子の分子間配置
図3 高分子の分子間配置
コラム3:共重合とポリマーアロイ
プラスチックXとプラスチックYとを混ぜて、中庸の性質の材料を作ることは広く行われています。copolymerization,その方法は図4に示すよう、2つあります。一つはX、Y両成分を分子内で混ぜるやり方で、これを共重合と言い、出来たものをコポリマーと言います。copolymers分子鎖を単一の成分だけで構成したものはホモポリマーと言われます。homopolymers.
もう一つのやり方は、別々に作った分子を後で混ぜる方法でポリマーアロイと言います。polymer alloyこれは金属の合金(alloy)にちなんだ呼び方です。
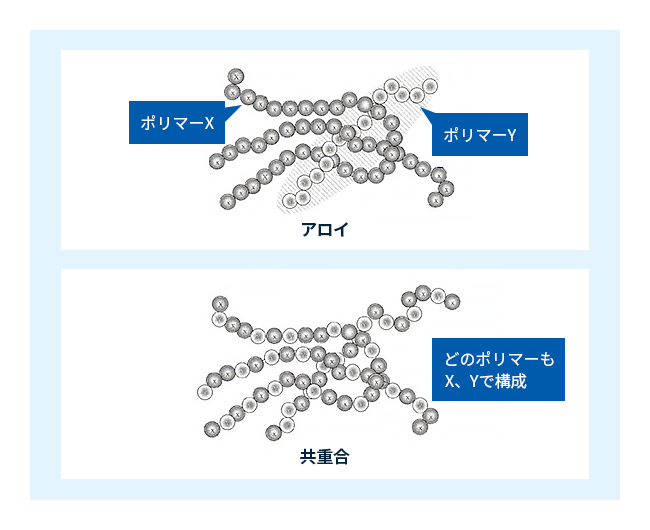 図4 共重合とポリマーアロイ
図4 共重合とポリマーアロイ
(出典:佐藤功 (2011) . ABCs of plastics プラスチックのいろは 日本工業出版)
(執筆:佐藤功、佐藤功技術事務所)
旭化成は、各種エンプラ製品の豊富なグレードラインナップと独自の技術力で、製品の性能向上を実現します。ご質問・ご相談・サンプルのご依頼など、お気軽にお問い合わせください。
製品・技術に関するご質問、サンプルのご依頼をお待ちしています