UL 94規格とは
プラスチックの難燃規格や試験方法などをご紹介します。

UL 94とは
UL 94とは、アメリカのULが認証している、電気機器および家電製品の部品に用いられるプラスチック材料の燃焼性試験の安全性に関する規格です。本ページでは、UL 94の特徴とその試験方法などをご紹介します 。
1.ULとは
ULとはアメリカの製品安全事業会社UL Solutionsまたは同社の発行している認証の略称です。UL SolutionsはULエンタープライズを構成する3つの組織の中の1つであり、かつてはUnderwriters Laboratories Inc., Underwriters Laboratories Limited Liability Company (UL LLC)という名称でした。認証対象は材料・部品・装置・道具類、最終製品にわたり、対象ごとに機能と安全性から独自の規格、評価方法を策定しています。対象品を申請すると規格に則り評価し、合格すると認証記号が与えられ、マークの使用が認められます。
ULの各種規格は提出された試料について試験をした結果があらかじめ設けられた規格を満たしたことを認証するもので、製品の保証を行っているわけではありません。申請者は合格したものに認証マークを表示することが出来ます。これによりユーザーの製品選択を支援することが出来ます。試験法が実質的で妥当なこと、運用が厳正なこと、抜き打ち検査などフォローアップがあることなどから多くの信頼・支持を集め、対象によっては業界規格に近い扱いを受けており、公的な規格にも影響を与えています。
プラスチックでは特に難燃性規格が世界的に認知されており、多くの公的規格が準用しています。このため、多くのプラスチック製品でUL認証状況が公表されています。
2.UL 94の特徴
UL 94は、規定の試験片を規定の手法で実際に燃やし、炎が消えるまでの時間等の状況からランク付けを行うことが特徴です。そのための試験片形状、状態、火源、燃焼法、燃焼状態によるランク付け、判定法が綿密に規定され、公表されています。
3.燃焼試験法
3-1.概要
試験には燃え広がる速さを見る「水平燃焼試験:HB」と、火が消えるまでの様子をみる「垂直燃焼試験:V」、大型製品など特に高い難燃性が求められる用途を想定した「5V試験」があります。燃焼時間および燃焼速度により、燃焼性評価を行います。
3-2.水平燃焼試験
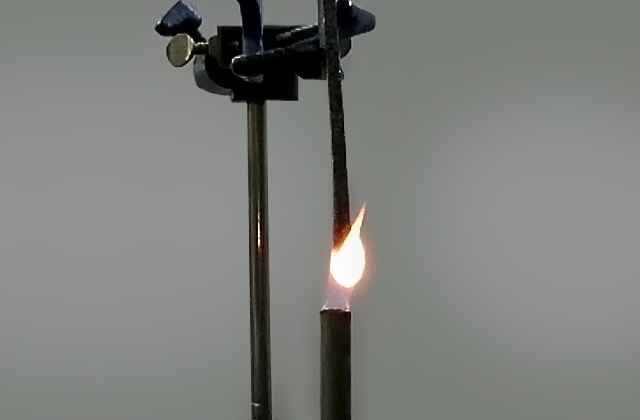
3-2-1.試験装置
概要を図1に示します。短冊状の試験片の一端をスタンドに短辺方向を45°傾けて水平に取り付けます。試験片の下には試験片から10±1mm離して滴下した溶融プラスチックを受ける20メッシュ金網を設けます。
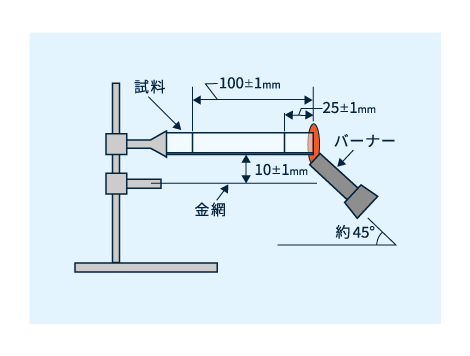 図1 水平燃焼試験法
図1 水平燃焼試験法
3-2-2.試験片
図2に示すような幅13.0±0.5mm、長さ125±5mm、厚みは申請する厚みの短冊状の試験片を使います(厚みは13mm未満が申請可能)。申請厚みの試験片を3枚使用します。試験片の前処理法は、23±2℃、50±10%RHで48時間以上と規定されており、着火する試験片端から25±1mmと100±1mmの位置に標線を引きます。
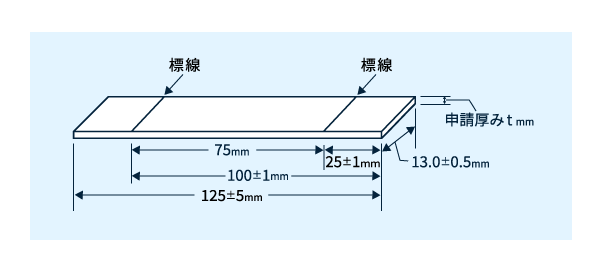 図2 試験片の形状
図2 試験片の形状
3-2-3.火源
水平燃焼試験には内径9.5mmブンゼンバーナーの炎長さを20mmに調整したものを使います。
3-2-4.試験法
30秒間バーナーの炎を試験片端6±1mmの場所にあて、30秒後に炎を遠ざけます。30秒以内に燃焼が25㎜標線に達した場合は、炎を試験片から離します。炎を遠ざけた後、25mm標線から100mm標線へ炎が到達する時間を測り燃焼速度を求めます。100mm標線まで炎が到達しない場合は炎が消える時間を計測し、25mm標線から燃焼した距離を測定します。
3-2-5.判定
下記のいずれかを満たすものは「UL 94HB」材料であると認証されます。
| 試験片厚み | 燃焼速度 |
|---|---|
| 厚みに問わず | 25mmまたは100mm標線到達前に燃焼が止まる |
| 3.0~13mm | 40mm/分以下 |
| 3.0mm未満 | 75mm/分以下 |
3-3.垂直燃焼試験
3-3-1.試験装置
図3に示すように、試験片が垂直になるよう、試験片上端をクランプに取り付けます。試験片下端から300±10mmはなれたところに外科用綿を敷きます。
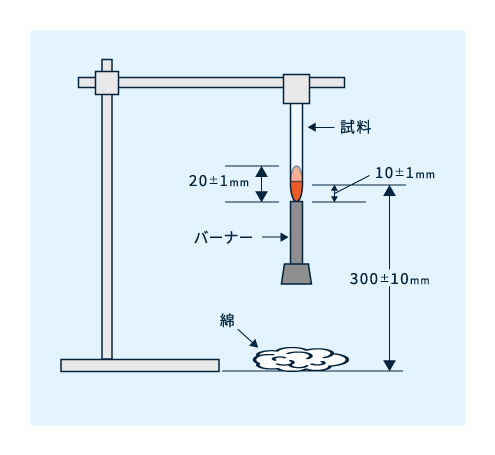 図3 垂直試験法
図3 垂直試験法
3-3-2.試験片
水平試験と同様に図2に示す短冊を各厚み5枚使用します。
3-3-3.火源
水平試験と同様で、内径9.5mmブンゼンバーナーの炎を高さ20mmに調整して使います。
3-3-4.試験法
図3の状態で試験片下端に炎をあてます。10秒間接炎後、炎を離します。炎を離した後、試験片の燃焼が30秒以内に止まったら、直ちにガスバーナーの炎をさらに10秒間あて、下記項目の燃焼時間、滴下物の有無、燃焼到達位置を5本の試験片について記録します。
- 第1回の試験炎をあてた後の火炎持続時間
- 第2回の試験炎をあてた後の火炎持続時間
- 第2回の試験炎をあてた後の火炎とグロー消滅時間
- 試験片が支持クランプまで燃えたかどうか
- 滴下した溶融物による綿の発火
3-3-5.判定
各項を満たすものがそれぞれ「UL 94 V-0、UL 94 V-1、UL 94 V-2」材料であると認証されます 。
| 判定項目 | UL 94 V-0 | UL 94 V-1 | UL 94 V-2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 各試験片の燃焼時間 | 10秒以下 | 30秒以下 | |
| 5本の合計燃焼時間 | 50秒以下 | 250秒以下 | |
| 各試験片のグロー消滅時間 | 30秒以下 | 60秒以下 | |
| 燃え上がり | クランプまで燃え上がらない | ||
| 敷綿の発火 | なし | あり | |
3-4.5V試験
3-4-1.概要5V試験はV-0、またはV-1ランクに適合した材料について行う燃焼試験です。短冊状の試験片で行う「垂直燃焼試験」と平板で行う「平板燃焼試験」から構成されています。
3-4-2.垂直燃焼試験
- 試験装置:
図4に示すように、短冊状試験片をクランプで垂直に固定します。ここへ20°傾けた炎をあてることが出来るようになっています。床には外科用綿を敷きます。
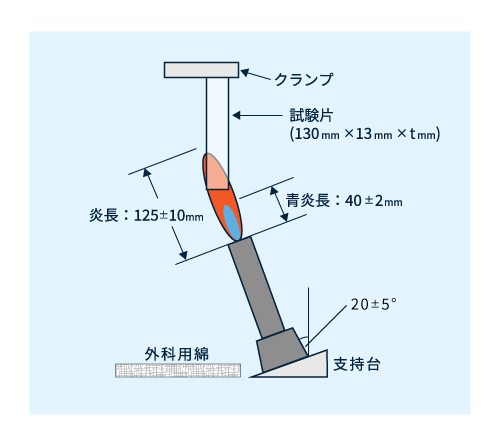 図4 5V垂直燃焼試験
図4 5V垂直燃焼試験
- 試験片:短冊で、図2に示した形状のものを使います。
- 火 源:内径9.5mmブンゼンバーナーを使い、炎を長さ125±10mm、青炎部長さ40±2mmに調整します。
- 試験法:短冊下端に炎を「5秒あて、5秒離す」、を5回繰り返し、短冊の燃え方を観察、記録します。
3-4-3.平板燃焼試験
- 試験装置:図5に示すように、150mm角の平板が水平に固定出来、平板中央に20°傾けた炎があてられるようになっています。
- 試験片:150㎜角の平板を用います。
- 火 源:短冊と同様の火炎長125mm±10mmに調整したガスバーナーを使用します。
- 試験法:平板下方中央に炎を5秒間あて、5秒引き離す操作を5回繰り返し、燃焼の様子を観察、記録します。
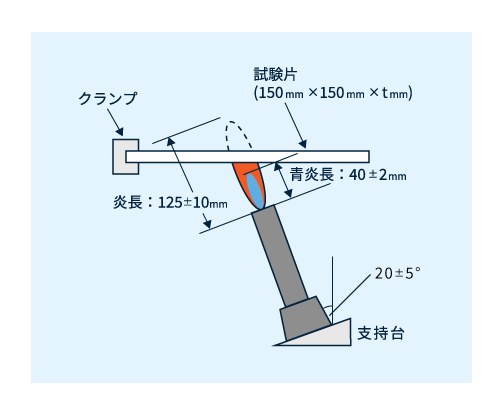 図5 5V平板試験
図5 5V平板試験
- 判定:各試験の結果下記を満たすものがそれぞれ「5VA」、「5VB」と認証されます。
| 項目 | 5VA | 5VB |
|---|---|---|
| 使用材料 | V -0またはV- 1に適合 | |
| 垂直燃焼試験 | 5回目の接炎後の燃焼+グロー時間が60秒以内 | |
| 滴下物によって脱脂綿が着火しない | ||
| 平板試験 | 孔が開かない | 孔があく |
上記試験により認証された製品には
- 登録コード(ID)の付与
- マーク表示許可
- 認証内容を記載したカード(UL Yellowcard、
旭化成のUL Yellowcard登録材料の検索はこちら)の発行が行われます。
最後に、プラスチックの燃焼試験にはUL以外にも業界固有のものもあります。
例えば、欧州の鉄道業界におけるEN 45545が挙げられます。鉄道をはじめとする公共交通機関では、トンネルや地下などの乗客の安全な避難が困難な状況で火災が発生することもあり得ます。このような場合、乗員が安全に列車を降りられるようになるまで、火災の拡大をできるだけ遅らせなければなりません。そのため、使用する材料の火災安全性に対する要求も高くなります。
EN 45545は、さまざまなハザードレベルを考慮した走行車両の防火要件を規定しており、欧州の法的枠組みとなっています。2013年に初版が発行され、欧州域内の鉄道では、適合が必須となっている他、アジア域内でも本規格相当の材料要求が徐々に広まりを見せています。EN 45545の中でも、EN 45545-2において材料・部品に関する要求が定められており、欧州鉄道に適用される製品においてはEN 45545-2に準拠した材料を用いることが求められます。
→ 欧州鉄道規格 EN 45545-2に適合した樹脂材料はこちら
(執筆:佐藤功、佐藤功技術事務所)
エンプラ業界ニュースをまとめてお届け!「エンプラトピックス」のご紹介
旭化成エンプラ総合情報サイトでは、多数の海外専門紙から厳選した、エンジニアリングプラスチック業界および技術動向の情報・ニュースをダウンロード形式で毎月お届けしています。当サイトの人気コンテンツです。
製品・技術に関するご質問、サンプルのご依頼をお待ちしています