01PA/CNF composite materials
PA/CNF composite materials combine Asahi Kasei’s heat-resistant CNFs with various types of PA. Key features of these materials include good sliding properties, good rigidity at both low and high temperatures, low specific gravity, and excellent reworkability compared to non-reinforced PA or PA/GF. PA/CNF composites are well-suited for use in fabricating sliding components with smaller sizes, thinner walls, and lighter weights.
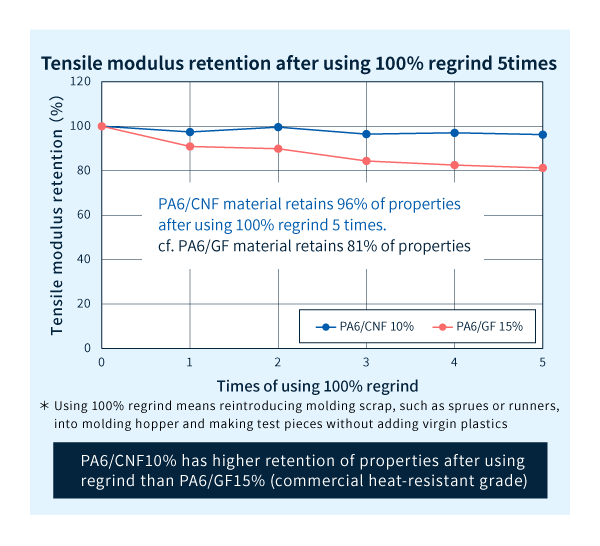
Feature 1: High heat resistance and mechanical properties retention after using regrind
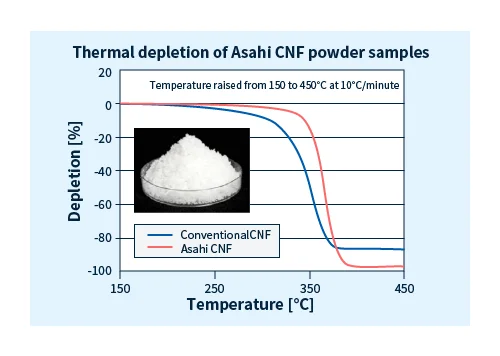
Asahi Kasei’s heat-resistant CNFs exhibit relatively low thermal degradation, fiber rupture and high mechanical properties retention after using regrind. Compared with conventional CNF, injection-molded products are less prone to coloration and have a superior appearance during molding (see figure below).

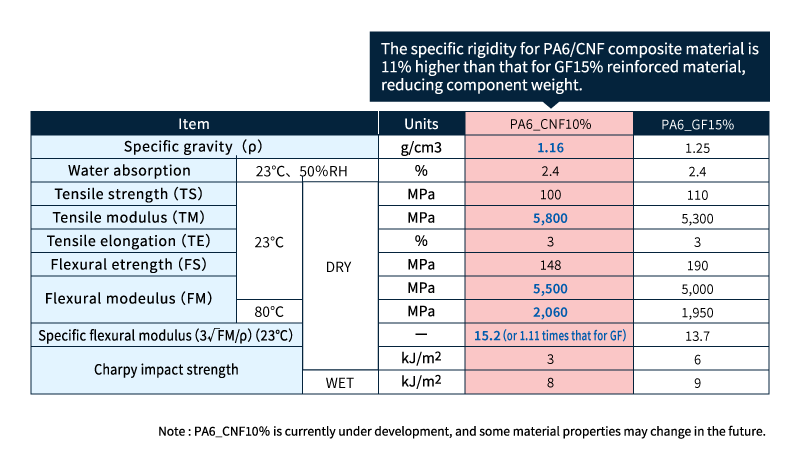
Feature 2: High rigidity and good dimensional stability
Asahi Kasei’s PA/CNF composite materials exhibits high specific flexural elasticity, high flexural modulus in the normal temperature range of 23°C to high temperature 80°C, and low coefficient of linear expansion compared to non-reinforced polyamide and glass fiber (GF) reinforced polyamide.
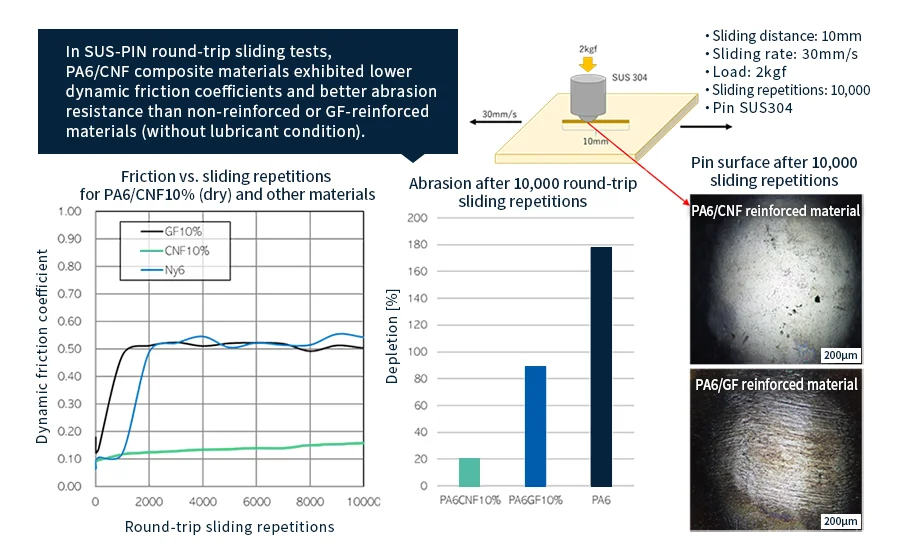
Feature 3: Good sliding properties
Asahi Kasei’s PA/CNF composite materials have low friction coefficients, exhibit low abrasion, and are less likely to abrade friction partners (such as metals).
Because CNF nanocomposite materials are less likely than glass-fiber-reinforced materials to abrade the metal surfaces over which they slide, these materials eliminate the need to treat those metal surfaces with special surface-processing steps.
Biomass plastic PA610/CNF composite
PA610 is a biomass engineering plastic containing polymers that are 60% plant-derived. Blending PA610 with 10% CNF reinforcers yields a composite with 65% plant-derived content. By using PA610 as the base polymer, the biomass raw material ratio is further increased, while still possessing the excellent reworkability, rigidity, dimensional stability, and sliding properties of PA/CNF as explained above.
⇒For more information on the plant-derived polyamide (PA) 610 LEONA™ BG series of products, click here.
POM/CNF composite materials
POM/CNF composite materials combine Asahi Kasei’s highly heat-resistant CNFs with POM. Key features of these materials include good sliding properties, good rigidity at high temperature, minimal shrinkage, a low coefficient of thermal expansion, and good creep properties at high temperature as compared to general POM. POM/CNF composite materials are well-suited for use in fabricating sliding components with smaller sizes, thinner walls, and lighter weights.
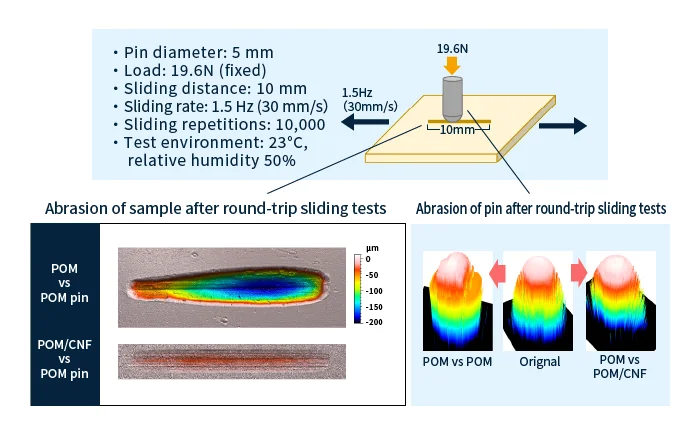
Feature 1: Superior sliding properties against surfaces made of metal or of the same material
POM has good mechanical properties, and exhibits superior friction and abrasion characteristics, making it a popular choice for fabricating gears and other sliding components. Also, CNFs are less likely than glass-fiber-reinforced materials to abrade metal partner surfaces in sliding components. Thus, POM/CNF composite materials combine good mechanical properties with improved sliding behavior.
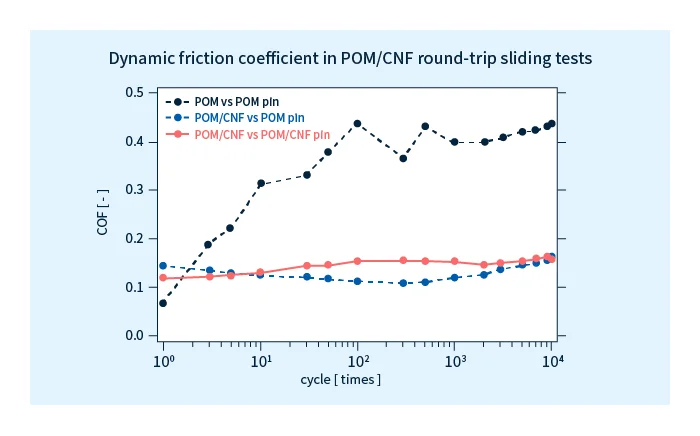
Moreover, even when used as sliding components against surfaces of the same material—a situation that is commonly understood to yield poor performance—POM/CNF components have low friction and low abrasion and operate silently, as indicated in the figure below. For this reason, choosing POM/CNF materials not only downsizes product, but also may allow multiple materials to be replaced by a single material.
Feature 2: High rigidity and good dimensional stability
In CNF nanocomposite materials, Asahi Kasei’s heat-resistant CNFs—which are based on cotton-linter constituents—are thoroughly dispersed within POM to form high-strength CNF networks throughout the resin, yielding superior rigidity and dimensional stability. POM/CNF composite materials, made with Asahi Kasei’s proprietary CNF dispersion technology, can retain their high rigidity even at high temperatures, where the rigidity of typical resins deteriorates.