Products
Excellent heat resistance, strength and toughness, insulation, and oil resistance. It is widely used in automotive parts, electrical and electronic parts.
Please request SDS and various certificates through a trading company or other purchasing channels.
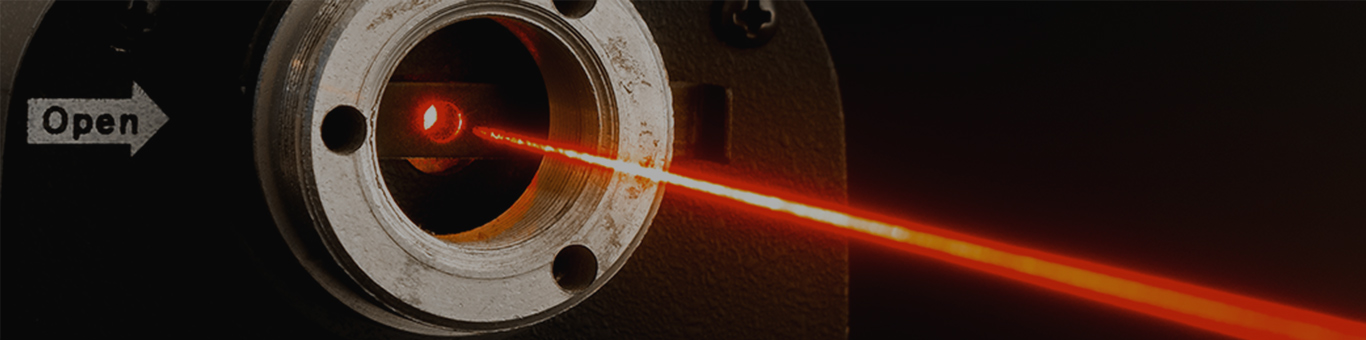
Laser welding is a technique that exploits the transparency of plastics to laser light. In this technique, laser light irradiating a target body (made of resin or plastic) generates heat at the interface between the body and a separate absorber layer to create welded junctions.
Asahi Kasei's engineering plastics, XYRON™, LEONA™, and TENAC™ can generally be laser welded by combining a natural material with a colored material (please feel free to contact us for more information on material and grade selection).
On this page, we propose LEONA™ SN Series as a resin material especially suitable for laser welding process. LEONA™ SN-series are halogen- and red phosphorus-free flame retardant polyamide resins featuring excellent laser transparency and capable of forming strong laser-welded joints.
 SN series
SN series
Asahi Kasei’s LEONA™ polyamide resins are engineering plastics featuring high strength and rigidity, and excellent thermal and chemical resistance. These materials may be strengthened by reinforcing with glass fibers or other fillers, improving strength, rigidity, durability, and dimensional stability.
LEONA™ SN-series are halogen & red phosphorus free flame retardant polyamide resins. These materials not only feature excellent laser transparency and the ability to form strong laser-welded junctions, but also offer superior performance in several other areas: high strength, high rigidity, compliance with the UL94 V-0 (0.75 mm) flammability standard, and (CTI) 600V (PLC 0) tracking resistance.
For laser light with a wavelength 940 nm, we compared the transmittance of SN11B—a LEONA™ SN-series with 25% glass-fiber reinforcement—to that of a general non-halogen flame-retardant polyamide (also with a glass-fiber content of 25%). The results showed that the transmittance of SN11B is approximately 2 times greater for natural-colored material and 3-4 times greater for black-colored material.
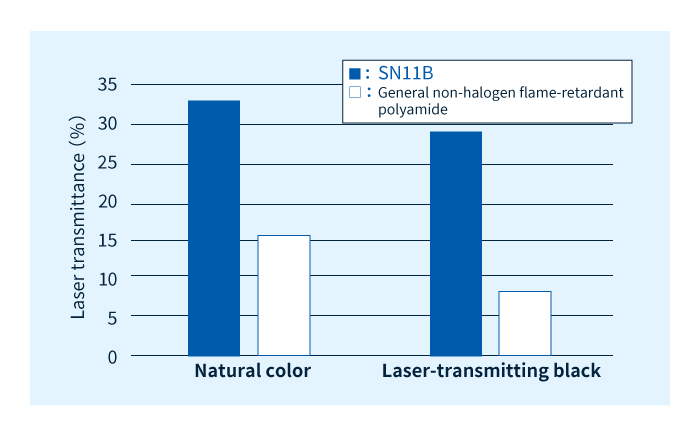
In laser welding, large quantities of energy pass through materials to arrive at the site of welded joints. LEONA™ SN-series offer the following advantages:
The figure below illustrates the excellent joint strength of compound parts formed by laser welding with LEONA™ SN-series.
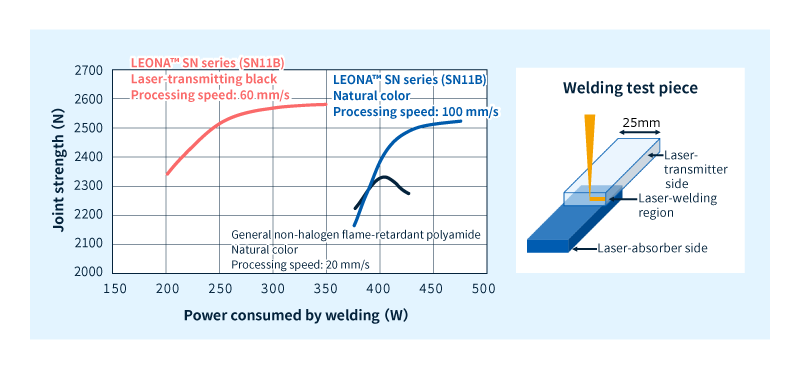
Compared to general non-halogen flame-retardant polyamide, LEONA™ SN-series with specialized black colorization, which transmits only laser light feature high laser-light transmittance and high joint strength.
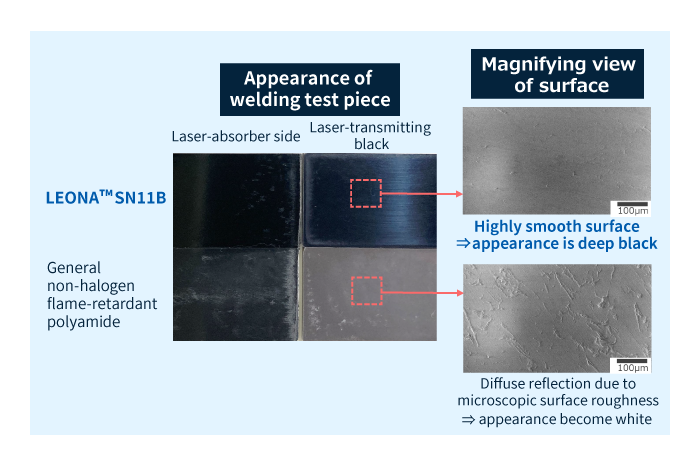
Moreover, in comparison to general non-halogen flame-retardant polyamide, LEONA™ SN-series with specialized black colorization feature an attractive deep-black appearance that makes them ideal for applications demanding stylish designs. The deep-black appearance of LEONA™ SN-series is due to the smoothness of their surfaces, which are free from microscopic surface roughness that gives rise to diffuse light reflection.
Switching to LEONA™ polyamide (PA) as the material for a battery case allowed the case to be manufactured via laser welding, reducing its size and weight.
Conventional welding methods such as vibration or ultrasonic welding entail significant vibrations that may damage sensitive components inside the case. Also, the use of screws or other fasteners requires that some portion of the case be dedicated to bosses or other fastener housings, increasing its spatial footprint. The use of laser welding eliminates such fasteners while avoiding damage to components inside the case, reducing its size and weight.

One promising application made possible by the improved laser transmittance of flame-retardant resin grades is laser welding of electronic components, for which conventional welding techniques are difficult to apply.
The ability to weld components with lower laser power reduces the emergence of unattractive “burned”-looking regions in welded surfaces.

Valves, pumps, electric parking brakes, ECU cases, vehicle-mounted cameras, and more
Asahi Kasei's engineering plastics products and technologies I'll introduce you in more detail.
We deliver product and industry information to help you gather information.