- TOP
- Sustainability
- リサイクルする

Sustainability
Recycling materials
Contents
Summary
- The recycling process for plastics may be classified into at least three different categories based on the method used, the material being recycled and its point of origin, and the type of products into which recycled materials are converted. Industry wide collaborative frameworks are emerging to ensure that efforts to promote plastic recycling—including techniques and quality standards for taking advantage of recycled materials as they are separated, as well as technologies to mitigate performance degradation—may be openly shared.
- Industry wide collaborative frameworks are emerging to ensure that efforts to promote plastic recycling—including techniques and quality standards for taking advantage of recycled materials as they are separated, as well as technologies to mitigate performance degradation—may be openly shared.
- Asahi Kasei is developing a broad products and technologies to promote recycling. Here we introduce recycled grades of our modified polyphenylene ether resins and lifetime-extending technology.
Classifying recycling schemes: Three perspectives
Many of the products we use in our daily lives depend on petroleum, metals, and other finite resources as raw materials. Precisely because these resources are finite, the ability to reuse discarded items as resources simultaneously helps to achieve two key goals—preserving resources and reducing waste—and for this reason we are seeing a worldwide acceleration of initiatives to recycle materials of every imaginable variety.
Here we focus in particular on plastic recycling. Recycling encompasses a broad range of concepts and terminologies and may give the impression of being difficult to understand, so we offer three complementary perspectives that are useful for thinking about this subject.

Three perspectives for classifying recycling schemes
There are various methods and types of plastic recycling, and it is possible to incorporate them according to each product. Here, we will introduce plastic recycling from three perspectives:
1.
By method used, 2. By material recycled and its point of origin, and 3. By the type of products into which recycled materials are converted.
1. Classifying recycling schemes by the methods used
In Japan, methods for recycling plastics may be classified into three primary categories.
■Material recycling (mechanical recycling) :
Discarded plastics are finely ground, melted, or otherwise processed and reused as materials for the same purpose as the original item.
■Chemical recycling (feedstock recycling) :
Discarded plastics are chemically decomposed and converted back into a form of raw material, which may be reused as an intermediate for new products.
■Thermal recycling (energy recovery) :
Discarded plastics are used either as a primary fuel or as an accelerant to produce combustion energy for electric-power generation. (This does not include burning of substances to reduce landfill volumes.)
2. Classifying recycling schemes by the material recycled and its point of origin
Recycling schemes may also be classified into two categories based on the material recycled and its point of origin.
■Post-consumer recycling (PCR):
After-market products are recovered and converted into reusable resources.
■Post-industrial recycling (PIR):
Pre-market materials produced in product manufacturing processes are recycled and reused.JIS Q 14021 (ISO 14021) refers to this as pre-consumer recycling.
*In manufacturing, waste products may be collected and reused in the same factory/production line at which they were generated. In the production of plastics, in particular, runners and sprues produced by molding are reused as regrind (as discussed in 02 Producing products). However, these practices are not included within the narrow definitions of the term recycling as specified by JIS Q 14021 (ISO 14021).
3. Classifying recycling schemes by the type of products into which recycled materials are converted
Finally, recycling schemes may be distinguished by the type of products into which recycled materials are converted.
■Horizontal recycling:
Recycled products are used to produce new products of the same type; for example, recycled PET bottles are used to produce new PET bottles (bottle-to-bottle recycling).
■Cascade recycling:
Recycled products are used to form new products of a different type. (In general, the recycled items are of lesser quality than the original products.)
Thus we see that methods of recycling come in many forms and may be extensively customized to handle various types of products. For this reason, industry-wide collaborative frameworks are emerging to ensure that efforts to promote plastic recycling—including techniques and quality standards established for taking advantage of recycled materials as they are separated, as well as technologies to mitigate performance degradation even after recycling—may be openly shared, and not confined within individual companies.
Asahi Kasei’s Recommended Solutions (1)
Recycling of modified PPE resin XYRON™
旭化成では、変性PPE樹脂 ザイロン™の製造時に、リサイクル原料を使いこなす技術・品質の確立、リサイクル後でも性能劣化しない技術の開発、オープンな協業体制の構築を推進しています。
Recycled grades of XYRON™ modified PPE resins
Asahi Kasei’s XYRON™ modified polyphenylene ether (modified PPE) resins are alloys and compound resins combining polyphenylene ether (PPE) with polystyrene (PS), polyamide (PA), polypropylene (PP), polyphenylene sulfide (PPS), and other plastics. Here, XYRON™ resins offer three specific advantages.
Features why XYRON™ resins for recycling
- Excellent resistance to heat and humidity ensure minimal degradation of physical properties during recycling
- Lowest specific gravity of all engineering plastics helps reduce CO2 emissions
- Easily combined with various other resins to form alloys or compounds; alloying with reused or recycled resins helps reduce usage of resources
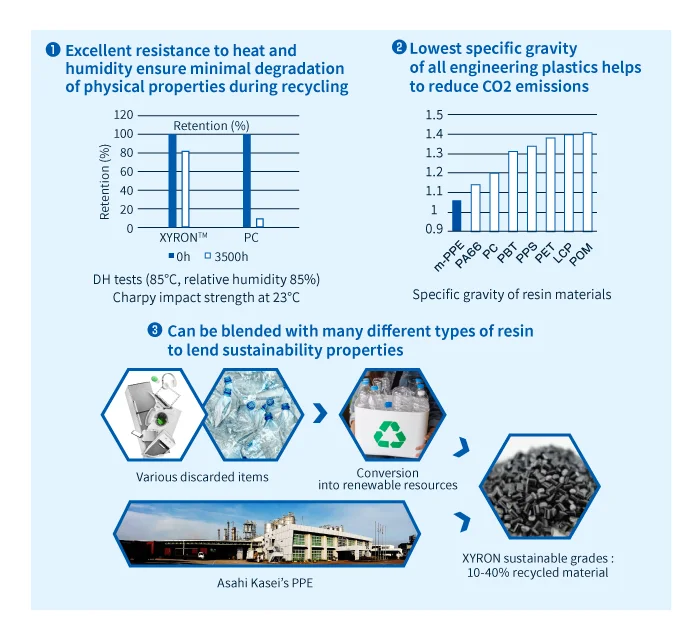
Features making XYRON
™
resins ideal for sustainability applications
XYRON™ recycled grades
XYRON™ recycled grades make use of resins from post-consumer recycling (PCR). We developed recycled grades containing 15-40% PCR content.
We are also developing new types of recycled alloys based on PCR resins.
Based on the concept of local production for local consumption, we aim to procure recycled resins at each production site.
In addition to minimizing carbon footprints, we are also paying careful attention to BCP (Business Continuity Plan) and logistics in establishing business systems.
We are also looking for partners for closed schemes, where we can develop more closely.
Going forward, Asahi Kasei is committed to developing XYRON™ resins for a broad range of solutions to meet the challenges of sustainable societies.
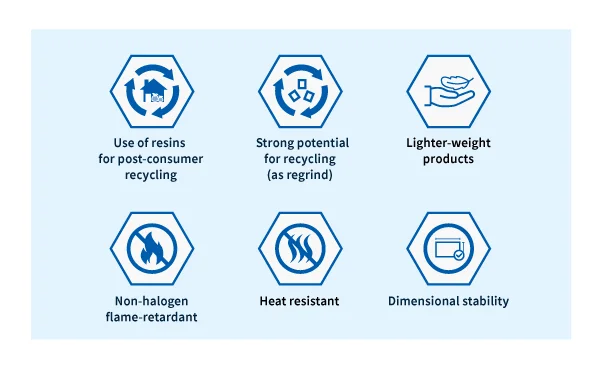
Key advantages offered by XYRON
™
recycled grades
Modified PPE made from PET bottles XYRON™ recycled PET/PPE alloy
.png)
Features making XYRON™ resins ideal for sustainability applications
Modified PPE XYRON™ PPE/RPS Sustainer Grade
Lifetime-extending technology minimizes degradation in recycling
The typical plastics exhibit performance degradation both during use in products and in recycling (reheating), yielding recycled material whose physical properties and flame retardance are inferior to those of “virgin material” in new and unused products.
XYRON™ modified polyphenylene ether resins incorporate unique lifetime-extending technology developed by Asahi Kasei to prevent degradation and maintain high performance both during use in modified polyphenylene-ether resin products and in recycling.
We recommend to choose XYRON™ resins with lifetime-extending technology which may enable closed-scheme circulation with high recycling rates, helping to realize circular economies. This technology can also be incorporated into existing XYRON™ products, allowing product lifetimes to be extended to meet the needs of your specific use case.
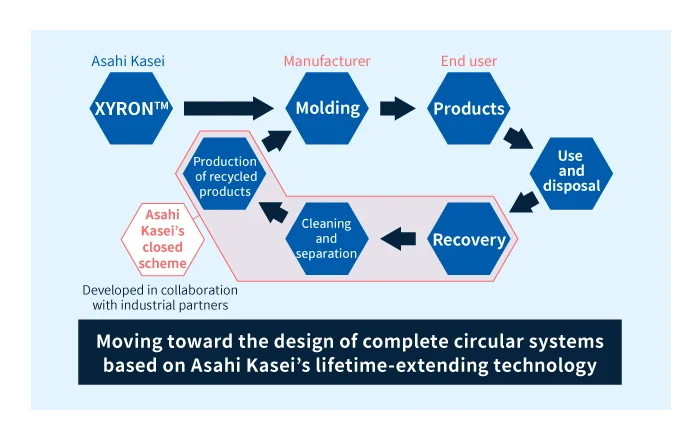
A closed-scheme recycling system made possible by Asahi Kasei’s lifetime-extending technology
Asahi Kasei's Recommended Solutions (2)
Introducing LEONA™ recycled grade polyamide resin
Asahi Kasei acquired the widely recognized international certification ISCC PLUS* for LEONA™ Polyamide (PA or Nylon) resin as a sustainable product at processing plant in Japan.
Polyamide is an engineering plastic widely used in automotive parts, home appliances, and industrial products. As awareness of the global environment and the importance of sustainability increases, Asahi Kasei is working to further raise the environmental contribution of LEONA™ Polyamide resin by promoting recycling efforts.
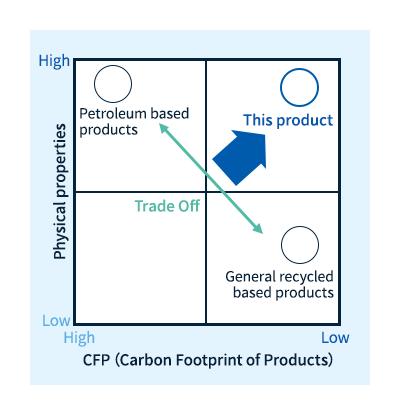
We have obtained ISCC PLUS certification for the scheme for compounding recycled pellets made from substandard products generated at our plant.By using recycled pellets made from substandard materials, it is possible to reduce CFP (Carbon Footprint of Products) and design according to customer requests while retaining the excellent performance (heat resistance, mechanical strength, etc.) of Polyamide resin.
*ISCC (International Sustainability and Carbon Certification) is an international certification system that offers solutions for the implementation and certification
*ISCC (International Sustainability and Carbon Certification) is an international certification system that offers solutions for the implementation and certification of waste and residue raw materials, non-bio renewables and recycled carbon materials and fuels. ISCC PLUS is a certification system that covers mainly bio-based carbon materials which are produced outside of the EU and supplied globally, and to manage and ensure sustainable raw materials in the supply chain.
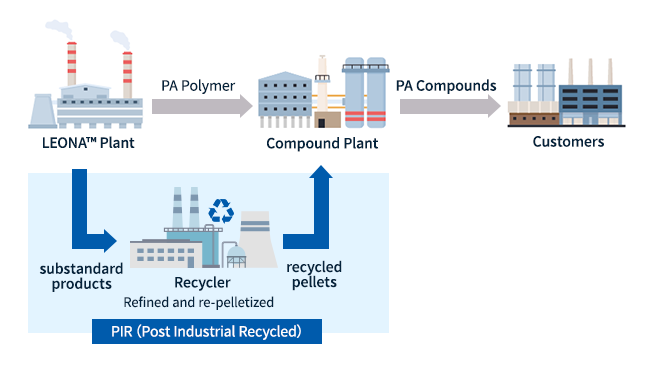
Scheme for compounding recycled pellets
Positioning of this product
Please contact us to ask questions and request samples. We look forward to hearing from you!









