product
Excellent self-lubricating nature, fatigue behavior, and oil resistance. It is used in gears, bearings, automotive interiors and medical parts.
For inquiries regarding SDS and various chemical substance investigations, please make your request through your purchasing route, such as via a trading company.
We appreciate your understanding and cooperation.

A 2014 white paper from Japan’s New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) defines robots as “intelligent mechanical systems equipped with three component technologies: sensors, actuators, and intelligent control systems.”*
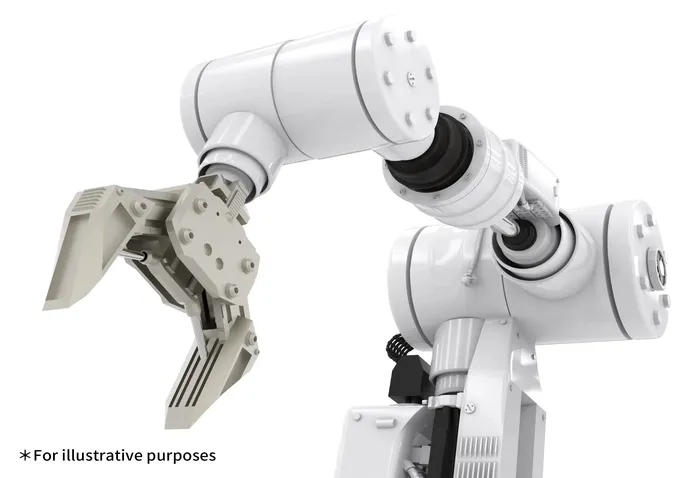
Robots may be further classified by the purpose they serve: robots used to replace work done by humans in industrial production and manufacturing environments are known as industrial robots, while robots that assist in providing services in areas such as medical care, logistics, shipping, cleaning, and housework are known as service robots.
Asahi Kasei supports the manufacturing efforts of our customers in the robotics industry by providing a range of materials with high-strength, high-rigidity, outstanding sliding behavior, excellent creep resistance, superior electrical properties. For example, choosing engineering plastics with properties appropriate for arms, reduction gears, actuators, motors, electrical components can help solve problems by reducing weight and lowering manufacturing costs.
The excellent mechanical properties and friction/abrasion behavior of polyacetal (POM) make it a common choice for mechanical components such as gears and bearings.
Asahi Kasei’s TENAC™ MG210 polyacetal resin is classified as a homopolymer, boasting excellent mechanical properties even compared to other POM materials. MG210 grades are based on homopolymers that offer durability properties–including creep resistance and fatigue behavior–superior to those of standard POM (copolymer), and TENAC™ MG210 grades improve these properties even more.
Asahi Kasei recommends to use TENAC™ MG210 polyacetal resin for mechanical components and other robot applications which may lead to extend product lifetimes and reduce product size
The CNFs developed by Asahi Kasei are biomass fibers containing cotton-linter constituents that are miniaturized via sophisticated techniques to sizes as small as nanometer scales. Asahi Kasei is developing technologies for nanodispersing CNFs in a variety of resins, ensuring a single, consistent manufacturing process from CNF production to CNF composites.
CPOM/CNF composite materials ombine Asahi Kasei’s highly heat-resistant CNFs with POM. Key features of these materials include good sliding properties, good rigidity at high temperature, minimal shrinkage, a low coefficient of thermal expansion, and good creep properties at high temperature as compared to general POM. POM/CNF composite materials are well-suited for use in fabricating sliding components with smaller sizes, thinner walls, and lighter weights.
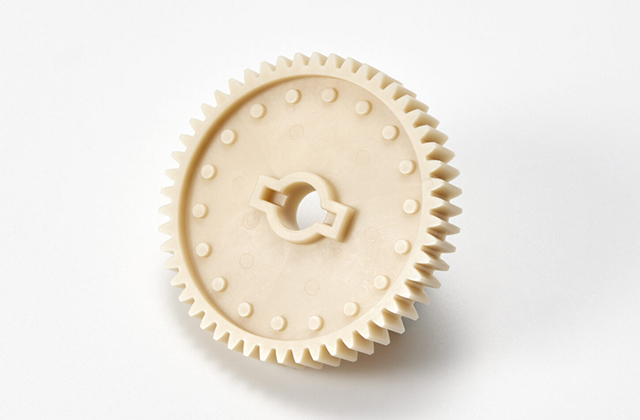

Reduction gears are mechanical converters that decelerate and transform rotational motion produced by motors to yield the required forces.
Asahi Kasei is developing materials that combine the good fatigue behavior of polyamides with outstanding friction and abrasion resistance.

Asahi Kasei’s XYRON™ modified polyphenylene ether (PPE) resins combine the usual flame retardance, dimensional stability, and heat resistance of modified PPE resins with vibration-control materials boasting high loss coefficients to lend good damping properties to the entire product lineup. We recommend to use vibration-control modified PPE resins with the high loss coefficient which may provide vibration-suppression effects that help to realize noise-suppressing designs.
Asahi Kasei’s engineering plastics are also useful for a broad range of other applications, including motor end caps, connectors, high-voltage components, and more. For more information, please contact us using the links below.
Asahi Kasei offers a wide range of simulation capabilities based on resin CAE technology to help you design products based on engineering plastics.
For example, switching from metal to engineering plastics for a robot arm or frame requires design optimization of product shapes to ensure satisfaction of all relevant strength requirements.
We offer simulation and optimization support–customized to accommodate the unique features of individual resins–to assist in your product design and manufacturing process.

Please feel free to contact us with any questions about our products or technologies or to request samples.
We will introduce Asahi Kasei 's engineering plastic products and technologies in more detail.
We regularly deliver product and industry information to help you gather information.